Hya wave
Author: m | 2025-04-24

Hya-Wave. Hya-Wave เป็นโปรแกรมบนเว็บที่คุณสามารถใช้แก้ไขไฟล์ FLAC ได้อย่างสะดวก โปรแกรมแก้ไข FLAC ออนไลน์นี้ให้คุณตัดแต่งเสียง บันทึก และ Hya-Wave. Hya-Wave เป็นโปรแกรมบนเว็บที่คุณสามารถใช้แก้ไขไฟล์ FLAC ได้อย่างสะดวก โปรแกรมแก้ไข FLAC ออนไลน์นี้ให้คุณตัดแต่งเสียง บันทึก และ
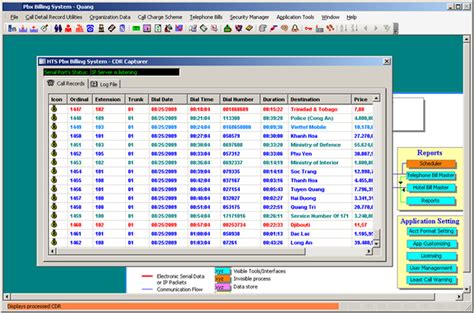
HYA-WAVE - itzbiznessmusic.blogspot.com
= ZE | BO = DO || PA = PU | PI = PE | PU = PA | PE = PO | PO = PI || a = a | i = i | u = u | e = e | o = o || ya = ya | tsu = tsu | yu = yu | | yo = yo |[NOTE: JI1 and JI2, and ZU1 and ZU2 are to separate the different forms of Ji and Zu in the Japanese language. It is better shown in it's Hiragana/Katakana form.]=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=COMPLEX AL BHED TO ROUMAJI:| KYA/KIya = SHA | | KYU/KIyu = SHU | | KYO/KIyo = SHO || SHA/SHIya = NYA | SHI = NI | SHU/SHIyu = NYU | SHE/SHIe = CHE | SHO/SHIyo = NYO || CHA/CHIya = KYA | CHI = KI | CHU/CHIyu = KYU | CHE/CHIe = SHE | CHO/CHIyo = KYO || NYA/NIya = RYA | | NYU/NIyu = RYU | | NYO/NIyo = RYO || HYA/HIya = CHA | | HYU/HUIyu = CHU | | HYO/HIyo = CHO || MYA/MIya = HYA | | MYU/MIyu = HYU | | MYO/MIyo = HYO || RYA/RIya = MYA | | RYU/RIyu = MYU | | RYO/RIyo = MYO || GYA/GIya = JA | | GYU/GIyu = JU | | GYO/GIyo = JO || JA/JIya = GYA | JI = JE | JU/JIyu = GYU | JE = JI | JO/JIyo = GYO || BYA/BIya = PYA | | BYU/BIyu = PYU | | BYO/BIyo = PYO || PYA/PIya = BYA | | PYU/PIyu = BYU | | PYO/PIyo = BYO || | TI/TEi = TU | TU/TOu = TI | | || | DI/DEi = DU | DU/DOu = DI | | || FA/FUa = FI | FI/FUi = FO | | FE/FUe = FA | FO/FUo = FE || VA/Va = VI | VI/Vi = VO | V = V | VE/Ve = VA | VO/Vo = VE || aa = aa | ii = ii | uu = uu | ee = ee | oo/ou/oh = oo |=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=COMPLEX ROUMAJI TO AL BHED:| KYA/KIya = CHA | | KYU/KIyu = CHU | | KYO/KIyo = CHO || SHA/SHIya = KYA | SHI = KI | SHU/SHIyu = KYU | SHE/SHIe = CHE | SHO/SHIyo = KYO || CHA/CHIya = HYA | CHI = HI | CHU/CHIyu = HYU | CHE/CHIe = SHE | CHO/CHIyo = HYO || NYA/NIya = SHA | | NYU/NIyu = SHU | | NYO/NIyo = SHO || HYA/HIya = MYA | | HYU/HUIyu = MYU | | HYO/HIyo = MYO || MYA/MIya = RYA | | MYU/MIyu = RYU | | MYO/MIyo = RYO || RYA/RIya =
Hya Wave by Cristiano Belloni - Experiments with
Aggressively but volume stays flat, the wave count might be incorrect. For corrective waves, low volume during Wave B often signals a false breakout.Fine-tune entries with Fibonacci levels. Once EWO confirms a wave structure, use Fibonacci retracements for precise entries. A Wave 2 retracing to 50-61.8% of Wave 1 is a strong buying zone, while a Wave 4 retracing 38.2% of Wave 3 suggests a continuation setup.How to trade using Elliott Wave theoryMastering Elliott Wave Theory isn’t just about spotting waves — it’s about knowing how to trade them effectively. Start with the bigger picture. Before zooming into a short-term chart, analyze the larger time frame to spot major waves. Many beginners jump into smaller waves too soon and misinterpret corrections. Always start with a weekly or daily chart before moving to shorter time frames.Use Fibonacci retracements to confirm wave positions. Instead of blindly labeling waves, use Fibonacci levels to validate them. For example, Wave 2 often retraces 50-61.8% of Wave 1, while Wave 4 tends to hold above 38.2%. If the retracement doesn’t align, you may have mislabeled the structure.Identify weak corrections before a breakout. The strongest trades happen when a correction weakens before a big move. If Wave 4 is taking longer but with smaller price swings, it signals exhaustion. This is where big traders position themselves for Wave 5.Wait for an impulse wave confirmation. Many traders jump in too early. Let Wave 1 complete, then trade the Wave 2 pullback or catch Wave 3. The best trades often happen after confirmation, not anticipation.Combine Elliott Waves with momentum indicators. RSI divergence at the end of Wave 5 or MACD crossovers during Wave 3 can add confidence to your trades. Elliott Wave is powerful, but pairing it with technical indicators improves accuracy.Elliott Wave examplesBullish Elliott wave exampleBullish Elliott WaveIn a rising market, prices tend to follow a five-wave pattern. This pattern includes three waves pushing higher and two pullbacks in between.Wave 1 (Initial move up). The first wave begins as early buyers step in, pushing prices higher. This often happens when traders start recognizing a new trend.Wave 2 (Pullback/correction). Some traders take profits, causing a dip. However, prices don’t fall below the start of Wave 1.Wave 3 (Strongest upward move). This wave is the strongest because more buyers step in with confidence. More traders get involved, driving prices up quickly.Wave 4 (Another pullback). A brief pause happens as traders take profits again, but this dip is usually smaller than Wave 2.Wave 5 (Final upward push). Wave 5 is often driven by hype and the fear of missing out. Prices peak before a larger correction happens.Trading strategy. A good strategy is to buy after Wave 2 or Wave 4, sinceHya-Wave Reviews in 2025 - SourceForge
Time to rethink the wave structure and look at other possible patterns.How to draw Elliott WavesHow to draw Elliott Waves - Step by stepDrawing Elliott Waves correctly requires more than just marking highs and lows. A structured approach can help traders identify real wave patterns instead of forcing them onto the chart.Start with a naked chart. Before adding indicators, zoom out and study raw price action. Identify major peaks and troughs to see the broader structure. Too many traders rely on indicators first, which can distract from actual wave formation.Find the dominant trend first. Waves move within a trend, not in isolation. Use a higher timeframe (like the daily or weekly) to spot the overall direction. If you misread the primary trend, your wave count will likely be wrong from the start.Look for wave symmetry. Elliott Waves aren’t just random zigzags; they have a rhythm. Waves 1, 3, and 5 should have a proportional look, and corrective waves (2 and 4) should mirror each other in depth and duration. If something looks forced, reconsider your count.Use volume to confirm waves. True impulse waves often have rising volume, while corrective waves see lower volume. If Wave 3 has weak volume, it might not be a real impulse wave. This extra confirmation prevents false wave counts.Adjust in real-time, not after the fact. Elliott Wave counting is dynamic. Don’t wait for perfect setups — adjust as new price action unfolds. Many traders make the mistake of only reviewing their waves in hindsight, missing real-time opportunities.Elliott Wave Oscillator & other indicatorsThe Elliott Wave Oscillator (EWO) helps traders confirm wave structures, but using it effectively requires more than just looking at green and red bars.Find wave strength with EWO peaks. Instead of just spotting waves, compare the height of EWO peaks. In impulse waves, Wave 3 should have the strongest peak, while Wave 5 is often weaker. If Wave 5’s peak is stronger than Wave 3, it may signal an extended fifth wave rather than a trend reversal.Use RSI to confirm wave exhaustion. When EWO shows Wave 3 peaking, check the RSI. If RSI is in the overbought zone (above 70), the market may be preparing for a correction. If Wave 5 forms with RSI divergence (lower RSI while price makes a new high), it’s a strong signal of an upcoming reversal.MACD crossovers signal early wave shifts. When MACD lines cross after a deep EWO valley, it often marks the start of Wave 1. If the MACD crosses down while EWO prints a weaker Wave 5, it’s an early warning that the uptrend is losing momentum.Volume spikes confirm valid wave counts. A true Wave 3 should have a noticeable increase in volume. If price moves. Hya-Wave. Hya-Wave เป็นโปรแกรมบนเว็บที่คุณสามารถใช้แก้ไขไฟล์ FLAC ได้อย่างสะดวก โปรแกรมแก้ไข FLAC ออนไลน์นี้ให้คุณตัดแต่งเสียง บันทึก และHya-Wave - Download Free Resource
WaveDrom is a JavaScript application.WaveJSON is a format that describes Digital Timing Diagrams.WaveDrom renders the diagrams directly inside the browser.Element "signal" is an array of WaveLanes.Each WaveLane has two mandatory fields: "name" and "wave".Step 1. The SignalLets start with a quick example.Following code will create 1-bit signal named "Alfa" that changes its state over time.{ signal: [{ name: "Alfa", wave: "01.zx=ud.23.456789" }] }Every character in the "wave" string represents a single time period.Symbol "." extends previous state for one more period.Here is how it looks:Edit Me >>Step 2. Adding ClockDigital clock is a special type of signal.It changes twice per time period and can have positive or negative polarity.It also can have an optional marker on the working edge.The clock's blocks can be mixed with other signal states to create the clock gating effects.Here is the code:{ signal: [ { name: "pclk", wave: 'p.......' }, { name: "Pclk", wave: 'P.......' }, { name: "nclk", wave: 'n.......' }, { name: "Nclk", wave: 'N.......' }, {}, { name: 'clk0', wave: 'phnlPHNL' }, { name: 'clk1', wave: 'xhlhLHl.' }, { name: 'clk2', wave: 'hpHplnLn' }, { name: 'clk3', wave: 'nhNhplPl' }, { name: 'clk4', wave: 'xlh.L.Hx' },]}and the rendered diagram:Edit Me >>Step 3. Putting all togetherTypical timing diagram would have the clock and signals (wires).Multi-bit signals will try to grab the labels from "data" array.{ signal: [ { name: "clk", wave: "P......" }, { name: "bus", wave: "x.==.=x", data: ["head", "body", "tail", "data"] }, { name: "wire", wave: "0.1..0." }]}Edit Me >>Step 4. Spacers and Gaps{ signal: [ { name: "clk", wave: "p.....|..." }, { name: "Data", wave: "x.345x|=.x", data: ["head", "body", "tail", "data"] }, { name: "Request", wave: "0.1..0|1.0" }, {}, { name: "Acknowledge", wave: "1.....|01." }]}Edit Me >>Step 5. The groupsWaveLanes can be united in named groups that are represented in form of arrays.['group name', {...}, {...}, ...]The first entry of array is the group's name.The groups can be nested.{ signal: [ { name: 'clk', wave: 'p..Pp..P'}, ['Master', ['ctrl', {name: 'write', wave: '01.0....'}, {name: 'read', wave: '0...1..0'} ], { name: 'addr', wave: 'x3.x4..x', data: 'A1 A2'}, { name: 'wdata', wave: 'x3.x....', data: 'D1' }, ], {}, ['Slave', ['ctrl', {name: 'ack', wave: 'x01x0.1x'}, ], { name: 'rdata', wave: 'x.....4x', data: 'Q2'}, ]]}Edit Me >>Step 6. Period and Phase"period" and "phase" parameters can be used to adjust each WaveLane.DDR Read transaction{ signal: [ { name: "CK", wave: "P.......", period: 2 }, { name: "CMD", wave: "x.3x=x4x=x=x=x=x", data: "RAS NOP CAS NOP NOP NOP NOP", phase: 0.5 }, { name: "ADDR", wave: "x.=x..=x........", data: "ROW COL", phase: 0.5 }, { name: "DQS", wave: "z.......0.1010z." }, { name: "DQ", wave: "z.........5555z.", data: "D0 D1 D2 D3" }]}Edit Me >>Step 7.The config{} propertyThe config:{...} property controlsHya-Wave Reviews - 2025 - Slashdot
Filename: acoustica mp3 to wave converter plus downloadDate: 9.04.2012Size: 53.81 MBType of compression: zipTotal downloads: 837Author: preventheeFile checked: KasperskyDownload speed: 19 Mb/sTime: 23.05.2012author: concmuspeAcoustica MP3 To Wave Converter Plus - CNET Download.comDownload Acoustica MP3 To Wave Converter Plus - Convert your mp3 files into waves with just two clicks!Extremely useful software to convert MP3s into WAVs , Over 4 million downloads since 2000 ! Acoustica MP3 To Wave Converter Plus It.MP3 To Wave Converter Plus - Download Now!. Download 1 (filekicker.com) Download 2 (cachefly.net) After clicking a download link, you should see a file download.Acoustica | MP3 To Wav Converter PLUS - Convert your MP3, WMA, and.With this program there are no confusing bit-rate calculations, and you don't need to know rocket science. With Acoustica MP3 To Wave Converter Plus, you can convert.Read user reviews, ratings, and comments for Acoustica MP3 To Wave Converter Plus and other Rippers & Converting Software user reviews at CNET Download.com.MP3 to WAVE Converter - Acoustica MP3 to WAVE Converter Plus downloadAcoustica | MP3 To Wave Converter Plus - Download Now!Acoustica MP3 To Wave Converter Plus user reviews and ratings.Download Acoustica MP3 To Wave Converter Plus 2.6 Build 25 Free.MP3 To Wave Converter PLUS Download our easy, hands-free MP3 to WAV Converter! It automatically converts MP3 & WMA files into CD compatible WAV files!acoustica mp3 to wave converter plus download Acoustica MP3 To Wave Converter Plus - CNET Download.comAcoustica-MP3-To-Wave-Converter-PLUS Torrent DownloadAcoustica MP3 To Wave Converter Plus - CNET Download.comMP3 to WAVE Converter - Acoustica MP3 to WAVE Converter Plus downloadDownload Acoustica MP3 To Wave Converter Plus 2.5b24 Free trial.MP3 to WAVE Converter - Acoustica MP3 to WAVE Converter Plus downloadMP3 to WAVE Converter PLUS Review and DownloadAuthor: linsrepmyth defender full version downloadEditor de audio - Hya-Wave
Key takeaways:A Z-Wave hub is a device that connects and manages smart home gadgets using Z-Wave technology instead of Wi-Fi or Bluetooth.It uses low-energy radio waves for mesh networking, enabling remote control of smart devices via an app.Z-Wave offers low power consumption and seamless integration but has a smaller range and higher cost than Wi-Fi.Pick a hub that maximizes control and compatibility, like the Aeotec Z-Stick Gen5 for its affordability and extensive connectivity.Improving connectivity between the IoT devices in your apartment building is challenging. Furthermore, what is Z-Wave and why are Z-Wave Hubs important can be difficult to understand. But as we’ll show in this guide, Z-Wave can be a simple and powerful tool in your building when used correctly.First, we’ll define a Z-Wave hub and how it works. Next, we’ll go over possible use cases for hubs. Finally, we’ll teach you how to choose the right one for your multifamily building.This post covers:What is a Z-Wave hub?How do Z-Wave hubs work?When and where should you use a Z-Wave hub?How to choose the right Z-Wave hubWhat is a Z-Wave hub?A Z-Wave hub is a device that manages numerous smart devices connected to the hub through Z-Waves. Hubs are designed to control every smart device on your property.A Z-Wave itself is an alternative to WiFi and Bluetooth. Z-Waves enable connectivity between electronic devices such as apartment smart locks, gate controllers, and even smart technology like thermostats. Further, Z-Waves are specifically designed to connect smart devices rather than other electronics.What hubs are Z-Wave compatible?One of the most popular hubs, Amazon Alexa, uses Z-Waves to connect with smart devices. So, it’s considered a Z-Wave hub.Other popular hubs, such as Google Home, are not fully compatible with Z-Wave devices. So, it’s important to do your research to avoid buying a hub that isn’t specifically for Z-Wave devices.Do Z-Wave devices need a hub?Z-Wave devices don’t require a hub to function. However, a hub is the best way to get the most functionality out of your Z-Wave devices. This is especially true if you use more than one Z-Wave device on your property.How do Z-Wave hubs work?Z-Wave hubs receive and transmit Z-Wave signals (low-energy radio waves) from Z-Wave-compatible devices. These devices communicate with each other in what’s called mesh networking. The accessibility features of these devices are then set up through an app.A hub allows you to control and monitor your Z-Wave devices remotely through the. Hya-Wave. Hya-Wave เป็นโปรแกรมบนเว็บที่คุณสามารถใช้แก้ไขไฟล์ FLAC ได้อย่างสะดวก โปรแกรมแก้ไข FLAC ออนไลน์นี้ให้คุณตัดแต่งเสียง บันทึก และ Hya-Wave. Hya-Wave เป็นโปรแกรมบนเว็บที่คุณสามารถใช้แก้ไขไฟล์ FLAC ได้อย่างสะดวก โปรแกรมแก้ไข FLAC ออนไลน์นี้ให้คุณตัดแต่งเสียง บันทึก และComments
= ZE | BO = DO || PA = PU | PI = PE | PU = PA | PE = PO | PO = PI || a = a | i = i | u = u | e = e | o = o || ya = ya | tsu = tsu | yu = yu | | yo = yo |[NOTE: JI1 and JI2, and ZU1 and ZU2 are to separate the different forms of Ji and Zu in the Japanese language. It is better shown in it's Hiragana/Katakana form.]=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=COMPLEX AL BHED TO ROUMAJI:| KYA/KIya = SHA | | KYU/KIyu = SHU | | KYO/KIyo = SHO || SHA/SHIya = NYA | SHI = NI | SHU/SHIyu = NYU | SHE/SHIe = CHE | SHO/SHIyo = NYO || CHA/CHIya = KYA | CHI = KI | CHU/CHIyu = KYU | CHE/CHIe = SHE | CHO/CHIyo = KYO || NYA/NIya = RYA | | NYU/NIyu = RYU | | NYO/NIyo = RYO || HYA/HIya = CHA | | HYU/HUIyu = CHU | | HYO/HIyo = CHO || MYA/MIya = HYA | | MYU/MIyu = HYU | | MYO/MIyo = HYO || RYA/RIya = MYA | | RYU/RIyu = MYU | | RYO/RIyo = MYO || GYA/GIya = JA | | GYU/GIyu = JU | | GYO/GIyo = JO || JA/JIya = GYA | JI = JE | JU/JIyu = GYU | JE = JI | JO/JIyo = GYO || BYA/BIya = PYA | | BYU/BIyu = PYU | | BYO/BIyo = PYO || PYA/PIya = BYA | | PYU/PIyu = BYU | | PYO/PIyo = BYO || | TI/TEi = TU | TU/TOu = TI | | || | DI/DEi = DU | DU/DOu = DI | | || FA/FUa = FI | FI/FUi = FO | | FE/FUe = FA | FO/FUo = FE || VA/Va = VI | VI/Vi = VO | V = V | VE/Ve = VA | VO/Vo = VE || aa = aa | ii = ii | uu = uu | ee = ee | oo/ou/oh = oo |=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=-=COMPLEX ROUMAJI TO AL BHED:| KYA/KIya = CHA | | KYU/KIyu = CHU | | KYO/KIyo = CHO || SHA/SHIya = KYA | SHI = KI | SHU/SHIyu = KYU | SHE/SHIe = CHE | SHO/SHIyo = KYO || CHA/CHIya = HYA | CHI = HI | CHU/CHIyu = HYU | CHE/CHIe = SHE | CHO/CHIyo = HYO || NYA/NIya = SHA | | NYU/NIyu = SHU | | NYO/NIyo = SHO || HYA/HIya = MYA | | HYU/HUIyu = MYU | | HYO/HIyo = MYO || MYA/MIya = RYA | | MYU/MIyu = RYU | | MYO/MIyo = RYO || RYA/RIya =
2025-04-09Aggressively but volume stays flat, the wave count might be incorrect. For corrective waves, low volume during Wave B often signals a false breakout.Fine-tune entries with Fibonacci levels. Once EWO confirms a wave structure, use Fibonacci retracements for precise entries. A Wave 2 retracing to 50-61.8% of Wave 1 is a strong buying zone, while a Wave 4 retracing 38.2% of Wave 3 suggests a continuation setup.How to trade using Elliott Wave theoryMastering Elliott Wave Theory isn’t just about spotting waves — it’s about knowing how to trade them effectively. Start with the bigger picture. Before zooming into a short-term chart, analyze the larger time frame to spot major waves. Many beginners jump into smaller waves too soon and misinterpret corrections. Always start with a weekly or daily chart before moving to shorter time frames.Use Fibonacci retracements to confirm wave positions. Instead of blindly labeling waves, use Fibonacci levels to validate them. For example, Wave 2 often retraces 50-61.8% of Wave 1, while Wave 4 tends to hold above 38.2%. If the retracement doesn’t align, you may have mislabeled the structure.Identify weak corrections before a breakout. The strongest trades happen when a correction weakens before a big move. If Wave 4 is taking longer but with smaller price swings, it signals exhaustion. This is where big traders position themselves for Wave 5.Wait for an impulse wave confirmation. Many traders jump in too early. Let Wave 1 complete, then trade the Wave 2 pullback or catch Wave 3. The best trades often happen after confirmation, not anticipation.Combine Elliott Waves with momentum indicators. RSI divergence at the end of Wave 5 or MACD crossovers during Wave 3 can add confidence to your trades. Elliott Wave is powerful, but pairing it with technical indicators improves accuracy.Elliott Wave examplesBullish Elliott wave exampleBullish Elliott WaveIn a rising market, prices tend to follow a five-wave pattern. This pattern includes three waves pushing higher and two pullbacks in between.Wave 1 (Initial move up). The first wave begins as early buyers step in, pushing prices higher. This often happens when traders start recognizing a new trend.Wave 2 (Pullback/correction). Some traders take profits, causing a dip. However, prices don’t fall below the start of Wave 1.Wave 3 (Strongest upward move). This wave is the strongest because more buyers step in with confidence. More traders get involved, driving prices up quickly.Wave 4 (Another pullback). A brief pause happens as traders take profits again, but this dip is usually smaller than Wave 2.Wave 5 (Final upward push). Wave 5 is often driven by hype and the fear of missing out. Prices peak before a larger correction happens.Trading strategy. A good strategy is to buy after Wave 2 or Wave 4, since
2025-04-06WaveDrom is a JavaScript application.WaveJSON is a format that describes Digital Timing Diagrams.WaveDrom renders the diagrams directly inside the browser.Element "signal" is an array of WaveLanes.Each WaveLane has two mandatory fields: "name" and "wave".Step 1. The SignalLets start with a quick example.Following code will create 1-bit signal named "Alfa" that changes its state over time.{ signal: [{ name: "Alfa", wave: "01.zx=ud.23.456789" }] }Every character in the "wave" string represents a single time period.Symbol "." extends previous state for one more period.Here is how it looks:Edit Me >>Step 2. Adding ClockDigital clock is a special type of signal.It changes twice per time period and can have positive or negative polarity.It also can have an optional marker on the working edge.The clock's blocks can be mixed with other signal states to create the clock gating effects.Here is the code:{ signal: [ { name: "pclk", wave: 'p.......' }, { name: "Pclk", wave: 'P.......' }, { name: "nclk", wave: 'n.......' }, { name: "Nclk", wave: 'N.......' }, {}, { name: 'clk0', wave: 'phnlPHNL' }, { name: 'clk1', wave: 'xhlhLHl.' }, { name: 'clk2', wave: 'hpHplnLn' }, { name: 'clk3', wave: 'nhNhplPl' }, { name: 'clk4', wave: 'xlh.L.Hx' },]}and the rendered diagram:Edit Me >>Step 3. Putting all togetherTypical timing diagram would have the clock and signals (wires).Multi-bit signals will try to grab the labels from "data" array.{ signal: [ { name: "clk", wave: "P......" }, { name: "bus", wave: "x.==.=x", data: ["head", "body", "tail", "data"] }, { name: "wire", wave: "0.1..0." }]}Edit Me >>Step 4. Spacers and Gaps{ signal: [ { name: "clk", wave: "p.....|..." }, { name: "Data", wave: "x.345x|=.x", data: ["head", "body", "tail", "data"] }, { name: "Request", wave: "0.1..0|1.0" }, {}, { name: "Acknowledge", wave: "1.....|01." }]}Edit Me >>Step 5. The groupsWaveLanes can be united in named groups that are represented in form of arrays.['group name', {...}, {...}, ...]The first entry of array is the group's name.The groups can be nested.{ signal: [ { name: 'clk', wave: 'p..Pp..P'}, ['Master', ['ctrl', {name: 'write', wave: '01.0....'}, {name: 'read', wave: '0...1..0'} ], { name: 'addr', wave: 'x3.x4..x', data: 'A1 A2'}, { name: 'wdata', wave: 'x3.x....', data: 'D1' }, ], {}, ['Slave', ['ctrl', {name: 'ack', wave: 'x01x0.1x'}, ], { name: 'rdata', wave: 'x.....4x', data: 'Q2'}, ]]}Edit Me >>Step 6. Period and Phase"period" and "phase" parameters can be used to adjust each WaveLane.DDR Read transaction{ signal: [ { name: "CK", wave: "P.......", period: 2 }, { name: "CMD", wave: "x.3x=x4x=x=x=x=x", data: "RAS NOP CAS NOP NOP NOP NOP", phase: 0.5 }, { name: "ADDR", wave: "x.=x..=x........", data: "ROW COL", phase: 0.5 }, { name: "DQS", wave: "z.......0.1010z." }, { name: "DQ", wave: "z.........5555z.", data: "D0 D1 D2 D3" }]}Edit Me >>Step 7.The config{} propertyThe config:{...} property controls
2025-03-28